Biomedical Waste Management: Safeguarding Health and the Environment
Biomedical waste, generated from healthcare facilities, research institutions, and laboratories, poses unique challenges due to its potential hazards. The effective management of biomedical waste is crucial to protect public health, healthcare workers, and the environment. This article delves into the various aspects of biomedical waste management, highlighting the importance of proper disposal and the role it plays in preventing the spread of infections and safeguarding the ecosystem.
Understanding Biomedical Waste:
Biomedical waste encompasses a wide range of materials, including infectious waste, sharps, pathological waste, pharmaceutical waste, and chemical waste generated during healthcare activities. It requires special attention and careful handling due to its potential to spread infections and pose risks to human health and the environment.
Classification of Biomedical Waste:
To streamline the management process, biomedical waste is categorized into different types based on its characteristics. This includes infectious waste, sharps waste, anatomical waste, chemical waste, pharmaceutical waste, and radioactive waste. Each category demands specific disposal methods to minimize risks.
Hazards of Improper Biomedical Waste Management:
Inadequate disposal of biomedical waste can lead to severe consequences. It poses a direct threat to healthcare workers, patients, and the general public through the potential transmission of infections. Moreover, untreated biomedical waste can contaminate air, water, and soil, causing long-term environmental damage and impacting biodiversity.
Legal Framework and Regulations:
Governments and international bodies have established strict regulations to govern the proper disposal of biomedical waste. Compliance with these regulations is mandatory for healthcare institutions and research facilities. Understanding and adhering to these guidelines is crucial for minimizing the environmental and public health impact of biomedical waste.
Best Practices in Biomedical Waste Management:
Implementing best practices in biomedical waste management involves a combination of segregation, collection, transportation, treatment, and disposal. Segregation at the source is the first step, ensuring that different types of waste are appropriately separated. Proper labeling and packaging of biomedical waste are essential to facilitate safe transportation and disposal.
Innovations in Biomedical Waste Treatment:
Technological advancements play a pivotal role in developing efficient methods for treating biomedical waste. Autoclaving, incineration, microwave treatment, and chemical disinfection are among the common techniques employed to render biomedical waste harmless. Ongoing research aims to discover more sustainable and environmentally friendly approaches to manage biomedical waste.
Community Awareness and Education:
Creating awareness among healthcare workers, waste handlers, and the general public is essential in fostering a culture of responsible waste management. Training programs, workshops, and educational campaigns help disseminate knowledge about the potential risks of biomedical waste and the importance of proper disposal.
Challenges and Future Directions:
Despite progress in biomedical waste management, several challenges persist. Limited infrastructure in certain regions, lack of awareness, and financial constraints hinder effective waste disposal. The need for continuous research and development in waste treatment technologies and sustainable practices is evident. Collaboration between governments, industries, and research institutions is essential to address these challenges and pave the way for more robust waste management systems.
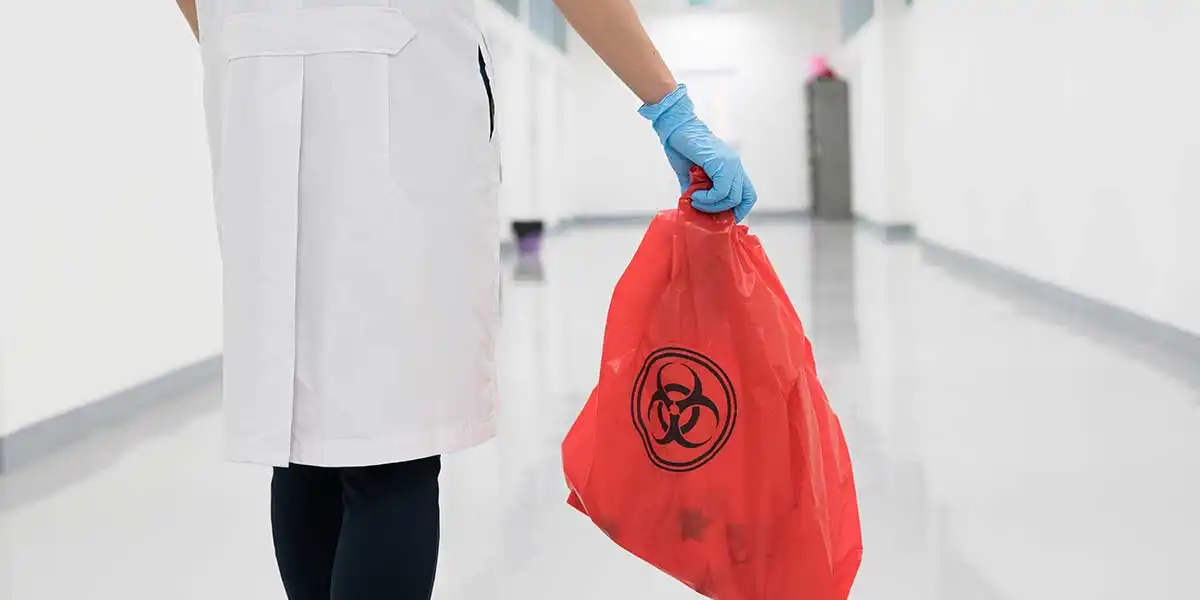

Global Perspectives on Biomedical Waste:
Biomedical waste is a global concern that transcends borders. Many countries, especially in the developing world, face significant challenges in implementing proper waste management practices. International cooperation and knowledge sharing can contribute to the development of standardized procedures, ensuring a consistent and effective approach to biomedical waste management worldwide.
The Role of Technology in Monitoring and Enforcement:
Advancements in technology offer new tools for monitoring and enforcing biomedical waste management regulations. Digital tracking systems, sensors, and artificial intelligence can be employed to trace the lifecycle of biomedical waste, ensuring that it is handled and disposed of in compliance with established guidelines. These technological solutions not only enhance accountability but also contribute to more efficient and transparent waste management practices.
Environmental Impact and Sustainable Practices:
The environmental impact of biomedical waste extends beyond immediate health concerns. As the world focuses on sustainability, there is a growing emphasis on adopting eco-friendly practices in waste management. From the development of biodegradable packaging for medical products to the promotion of recycling in healthcare settings, incorporating sustainability into biomedical waste management practices is an evolving aspect of the field.
Educating the Next Generation:
To cultivate a lasting impact on biomedical waste management, integrating education on waste reduction and proper disposal into medical and scientific curricula is crucial. Future healthcare professionals and researchers should be equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary to minimize waste generation and handle biomedical waste responsibly, contributing to a sustainable healthcare ecosystem.
Conclusion: Towards a Sustainable Future:
Biomedical waste management is a complex and dynamic field that requires constant adaptation to emerging challenges and technologies. As we move forward, it is essential to view waste management not only as a regulatory obligation but as a shared responsibility to protect human health and the environment. By embracing innovation, fostering awareness, and promoting sustainable practices, we can pave the way for a future where biomedical waste is effectively managed, ensuring a healthier world for generations to come.
Biomedical waste management is a critical aspect of public health and environmental protection. Adhering to regulations, implementing best practices, and embracing technological innovations are essential steps towards minimizing the impact of biomedical waste. A collective effort from healthcare institutions, regulatory bodies, and the community is necessary to ensure a safe and sustainable approach to biomedical waste management, ultimately safeguarding both human health and the environment.